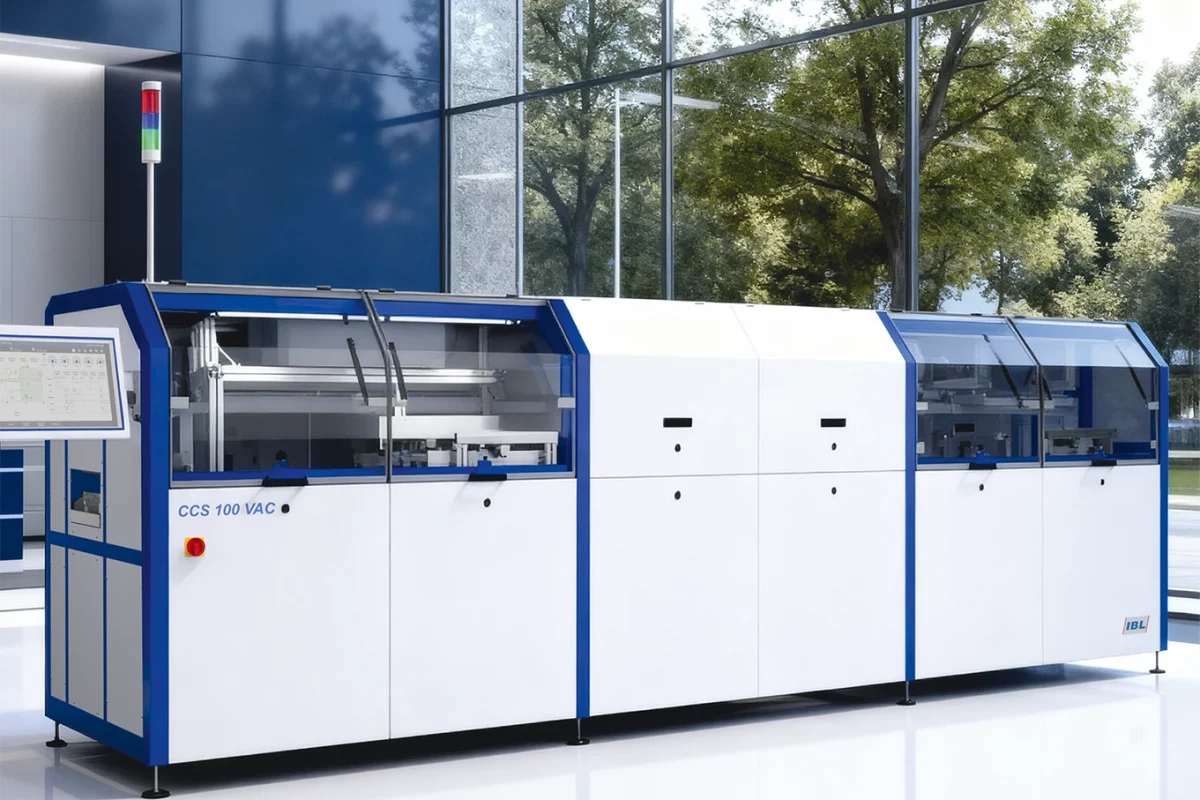
Vapour phase soldering is particularly suitable for applications where the highest soldering quality, reliable temperature control and gentle handling of sensitive components are required. It is typically used in the following areas:
In medical technology, the process is used to reliably solder complex assemblies with sensitive sensors, microchips or high-density layouts, with maximum process stability and without thermal overload. Similar requirements apply in the aerospace industry, where electronic systems have to withstand extreme loads and error rates must be close to zero. Here, vapour phase soldering has established itself as the preferred process due to its even heat distribution and reproducibility.
The process is also widely used in defense technology and is used in particular for safety-critical electronics with heterogeneous components and varying thermal mass. The reliable soldering quality without the use of sensitive temperature profiles makes the process particularly attractive.
In the automotive industry, vapour phase soldering is used for control units, sensors or power electronics, for example, especially when complex or high-density assemblies with different thermal requirements need to be processed. Prototype construction and small series production also benefit from the flexibility and process reliability of the method, especially when component geometries or batch sizes vary. Complex programming of the heat input and preparation of the system are generally not necessary, as the same soldering profile can often be used.
In addition, vapour phase soldering is preferred for high-frequency electronic assemblies, power-dense PCBs or high-quality measurement technology, i.e. wherever conventional soldering processes reach their limits. The combination of freedom from oxidation, controlled temperature management and uniform heating makes the process ideal for the production of sophisticated, high-quality electronics.